MODULE 3 - SECTION 7
FLASH CARDS for the DORSAL COLUMN - MEDIAL LEMNISCUS PATHWAY
In this computer version of flash cards, questions alternate with answers as you scroll down the page. We suggest that you limit the height of your viewing window so that you can't see the answers until you have made your own choices. In this first exercise, we just ask you to identify structures or spaces. In future sets of flash cards we expect to use the blue boxes on the right to ask functional questions.
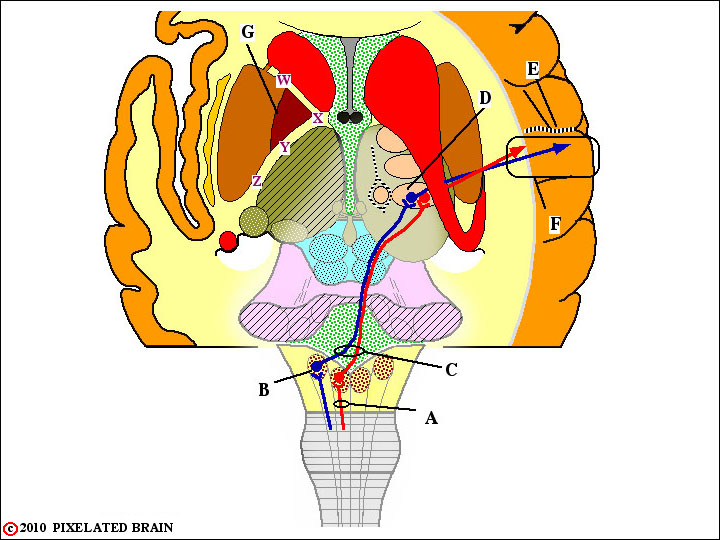
QUESTION 1
A - Identify this bundle of ascending axons. They convey sensory information from what part of the body?
B - Identify this nucleus.
C - Name this part of the pathway.Why is its location of great importance?
D - Name this nucleus.
E - Name this cortical sulcus.
F - Name this cortical gyrus.
G - Which of these letters (W X Y Z) best marks the position of this pathway in the internal capsule?

ANSWER 1
A - Identify this bundle of ascending axons. The fasciculus gracilis They convey sensory information from what oart of the body? Body below T6.They convey sensory information from what part of the body?
B - Identify this nucleus. Nucleus cuneatus.
C - Name this part of the pathway.The decussation of the medial lemniscus. Why is its location of great importance? Lesions below this level cause an ipsilateral sensory loss; lesions above cause a contralateral loss.
D - Name this nucleus.The nucleus ventralis posterolateralis.
E - Name this cortical sulcus. The central sulcus.
F - Name this cortical gyrus. The postcentral gyrus.
G - Which of these letters (W X Y Z) best marks the position of this pathway in the internal capsule? Z.
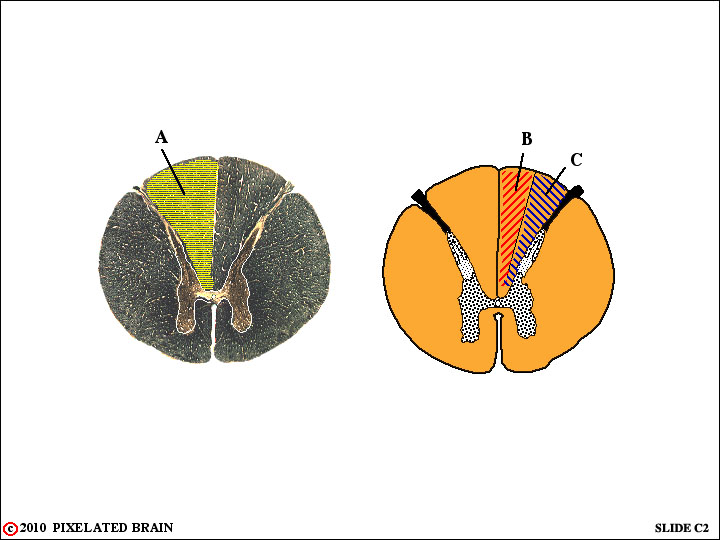
QUESTION 2
A - Identify. Where are the cell bodies that contribute axons to this part of the spinal cord? Are all the axons ascending (to the brainstem), descending, or a mixture of both?
B - Identify. Where will most of these axons terminate? What kind of information do they convey?
C - Identify. Where will most of these axons terminate? Will the axons cross the midline before terminating. Describe the loss in function, and the part of the body involved, if this pathway were damaged at ttis level.
D -
E -
F -
G -

ANSWER 2
A - Identify. The dorsal (or posterior) funiculus. Where are the cell bodies that contribute axons to this part of the spinal cord? In dorsal root ganglia. Are all the axons ascending (to the brainstem), descending, or a mixture of both? Ascending, only.
B - Identify. The fasciculus gracilis. Where will most of these axons terminate? In the nucleus gracilis. What kind of information do they convey? Fine (discriminative) touch and position senses.
C - Identify. The fasciculus cuneatus. Where will most of these axons terminate? In the nucleus cuneatus. Will the axons cross the midline before terminating. No! Describe the loss in function, and the part of the body involved, if this pathway were damaged at ttis level. Loss of fine touch and position information from the ipsilateral (same) side of the body between C2 and T6.
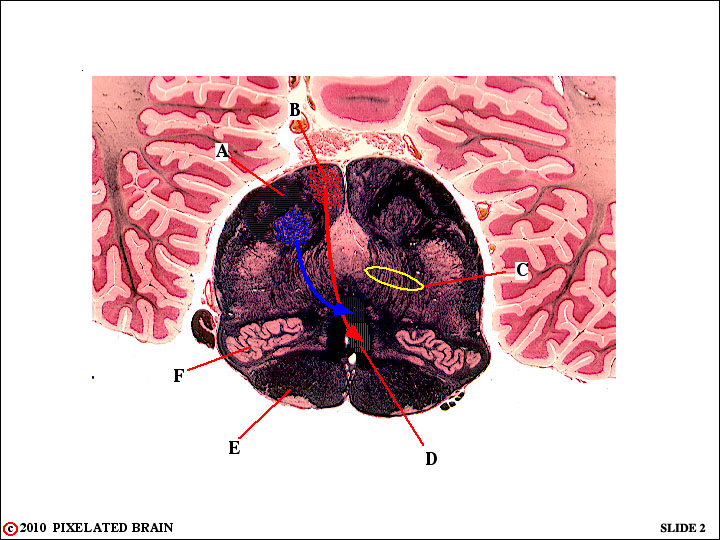
QUESTION 3
A - Identify this bundle of (blue) axons. Where will they terminate? Where will they terminate?
B - Identify this nucleus.
C - What name is given to the fibers enclosed within this oval?
D - Where (in what nucleus) will the axons in this pathway terminate?
E - Identify. What do you know about this structure (see module 2)?
F - Identify. What do you know about this structure (see module 2)?

ANSWER 3
A - Identify this bundle of (blue) axons. The fasciculus cuneatus. Where will they terminate? In the nucleus cuneatus.
B - Identify this nucleus. The nucleus gracilis.
C - What name is given to the fibers enclosed within this oval? Internal arcuate fibers.
D - Where (in what nucleus) will the axons in this pathway terminate? In the nucleus ventralis posterolateralis.
E - Identify. The pyramid. What do you know about this structure (see module 2)? It is a descending motor pathway.
F - Identify. The inferior olive .
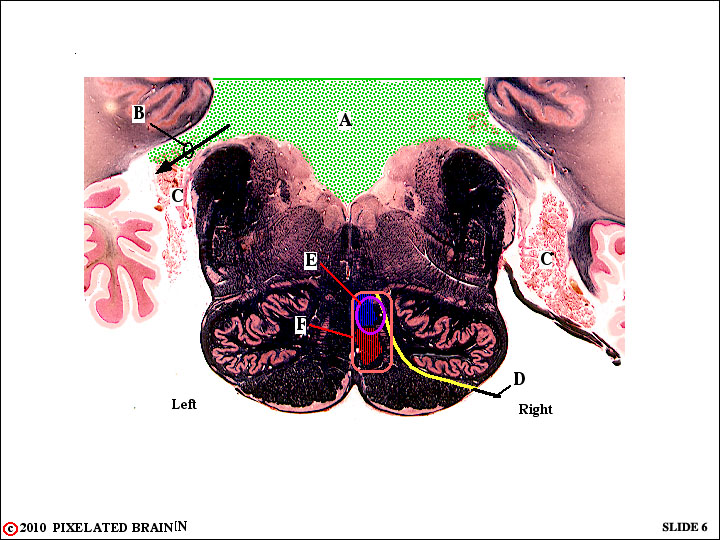
QUESTION 4
QUESTIONS FROM PAST MODULES
A - Identify this fluid-filled space.
B - Identify this passage way.
C - Identify this filmy vascular tissue.
QUESTIONS FROM MODULE 3
E - We have decided previously (Review 2, question 4) that D must be the hypoglossal nerve. Now we tell you that this nerve supplies innervation to the muscles of the ipsilateral side of the tongue and we show you, in yellow, the course of the nerve fibers prior to their point of exit from the brainstem.
E - What loss in function would you expect in an individual who developed this lesion?
F - What loss in function would you expect if the lesion expanded to this size?

ANSWER 4
QUESTIONS FROM PAST MODULES
A - Identify this fluid-filled space. The Fourth Ventricle.
B - Identify this passage way. The Foramen of Luschka.
C - Identify this filmy vascular tissue. Choroid Plexus. This tissue forms the roof of the posterior part of the fourth ventricle and some of it extends out through the foramen.
QUESTIONS FROM MODULE 3
E - What loss in function would you expect in an individual who developed this lesion? Loss in motor function on the right side of the tongue and loss of fine touch and position senses on the left side of the body, in the region above T6. The sensory loss is due to destruction of the cuneate component of the medial lemniscus - blue in the above figure.
F - What loss in function would you expect if the lesion expanded to this size? Sensory loss extends to involve the entire left side of the body, because of the added destruction of the gracile component of the medial lemniscus - red in the figure.
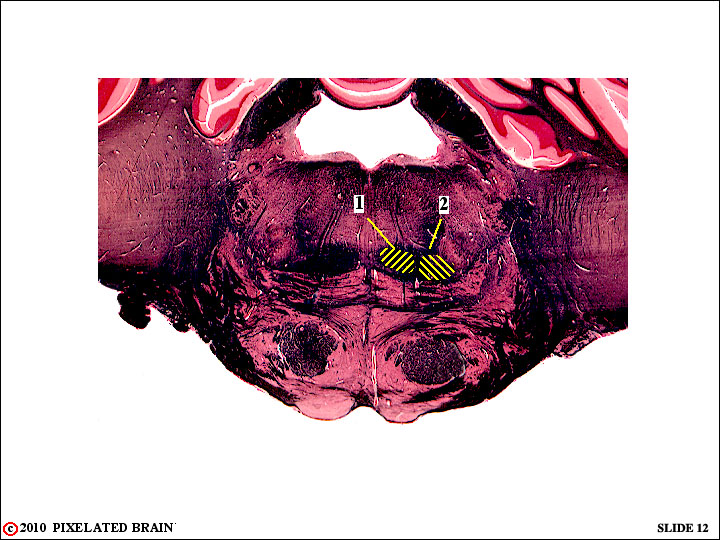
QUESTION 5
A - 1 and 2 are components of what pathway?
B - Where (in what nucleus) are the neurons that contribute axons to 1.
C - Are the axons of 1 and 2 part of 1st, 2ond or 3rd order neurons in this sensory pathway?
D - In what nucleus will all these axons terminate?
E - Which axons will terminate more laterally in this nucleus - those in 1 or those in 2?
F - These neurons (the ones terminating more laterally) convey sensory information from what part of the body?
G -

ANSWER 5
A - 1 and 2 are components of what pathway? The medial lemniscus.
B - Where (in what nucleus) are the neurons that contribute axons to 1?In the nucleus cuneatus.
C - Are the axons of 1 and 2 part of 1st, 2ond or 3rd order neurons in this sensory pathway? 2ond order.
D - In what nucleus will all these axons terminate? The nucleus ventralis posterolateralis (VPL).
E - Which axons will terminate more laterally in this nucleus - those in 1 or those in 2? Those in 2 .
F - These neurons (the ones terminating more laterally) convey sensory information from what part of the body? The contralateral side of the body, below T6.
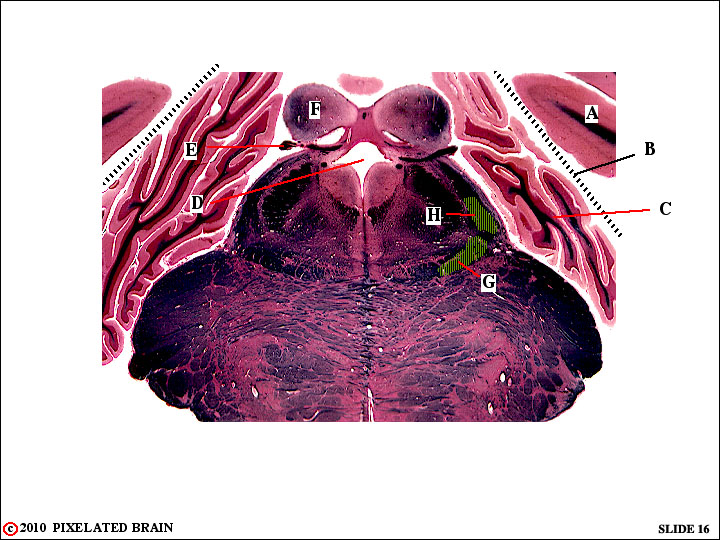
QUESTION 6
1 Identify :
A -
B -
C -
D -
E -
F -
2 Where do the following pathways originate?
G -
H -
3 This slide passes through what part of the brainstem?
4 This part of the brain lies in which cranial fossa?

ANSWER 6
1 Identify :
A - cerebral hemisphere
B - tentorium cerebelli
C - cerebellar hemisphere
D - transition from 4th ventricle to cerebral aqueduct
E - trochlear nerve
F - inferior colliculus
2 Where do the following pathways originate?
G - nucleus gracilis
H - nucleus cuneatus
3 This slide passes through what part of the brainstem? - this is an oblique cut; the lower part of the section passes through the pons and the upper part passes through the midbrain.
4 This part of the brain lies in which cranial fossa? - the posterior cranial fossa.
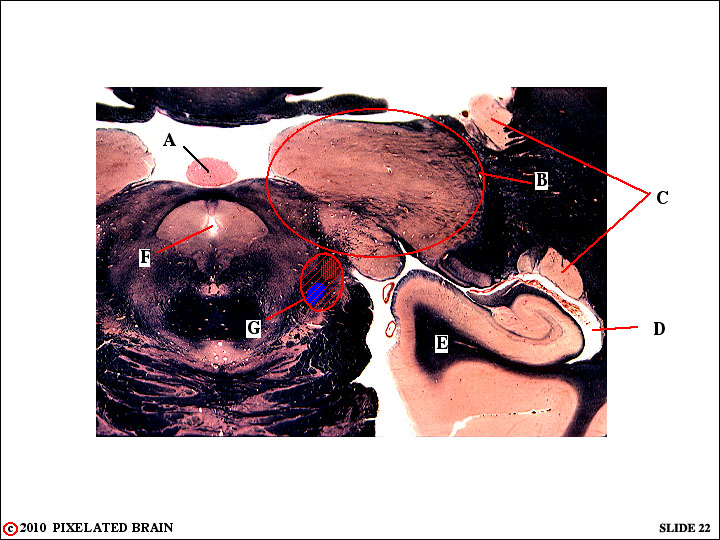
QUESTION 7
1 Identify the following:
A -
B -
C -
D -
E -
F -
G -
2 Based on what we have covered so far, what sensory loss would you expect following lesion G?

ANSWER 7
1 Identify the following:
A - the pineal
B - the thalamus
C - the tail of the caudate nucleus, cut twice as it curls down and around, following the lateral ventricle into the temporal lobe
D - the inferior horn of the lateral ventricle
E - the medial edge of the temporal lobe
F - the cerebral aqueduct
2 Based on what we have covered so far, what sensory loss would you expect following lesion G? This lesion gets the entire medial lemniscus as it approaches the thalamus. The result would be a loss of fine touch and proprioception involviing the contralateral body, below the head. In fact, the sensory loss would be more extensive because of associated damage to pathways we will be taking up in Module 4.
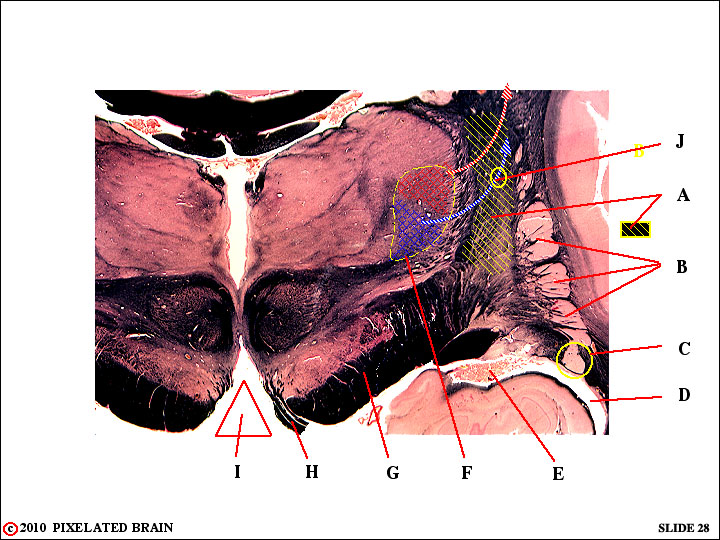
QUESTION 8
1 - Identify:
A -
B -
C -
D -
E -
F -
G -
H -
I -
2 - Tell us all you know about J.

ANSWER 8
1 - Identify:
A - internal capsule
B - putamen
C - tail of caudate nucleus
D - inferior horn of lateral ventricle
E - choroid plexus
F - nucleus ventralis posterolateralis (VPL)
G - cerebral peduncle
H - oculomotor nerve
I - interpeduncular fossa
2 - Tell us all you know about J. J traces the course of the axon of a third order sensory neuron having its cell body in VPL. The axon is seen departing from the nucleus and entering the internal capsule to ascend, terminating in the S1 region of the postcentral gyrus. It will terminate medial to the red fiber above it, and conveys sensory information from the upper body (above T6).