MODULE 6 - SECTION 4 - INPUT from the CEREBRAL CORTEX
We will now try to trace the pathways on our slides. But first let's look at two views that show how the cortical input is organized.
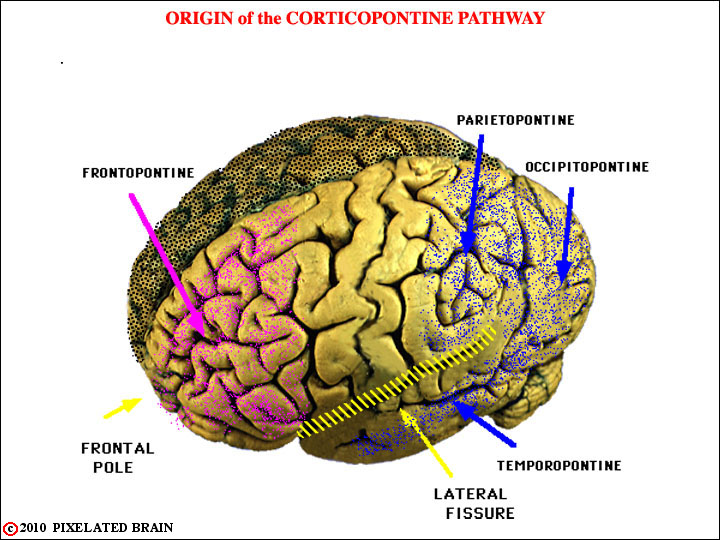
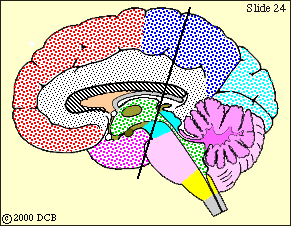
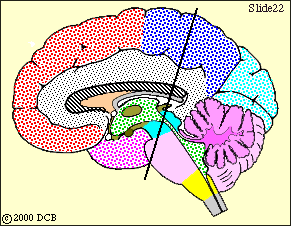
This view shows the broad origin of the cortical input to cerebellum. The descending pathway from the frontal lobe is colored violet in subsequent views and that from the other lobes is colored dark blue.
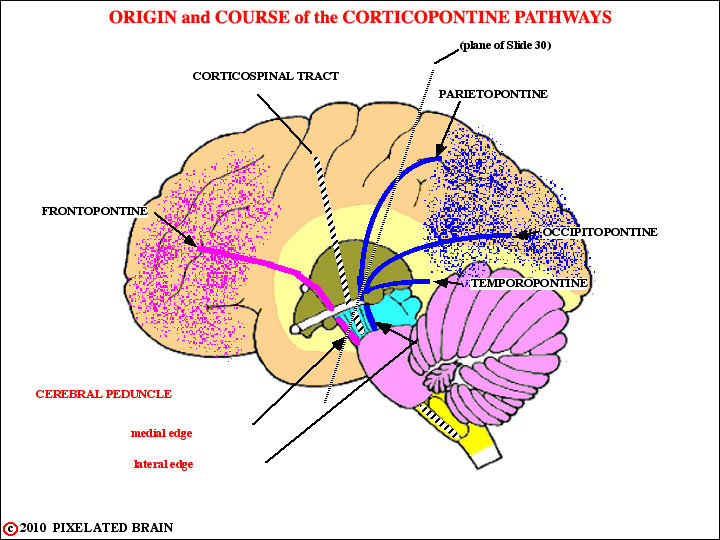
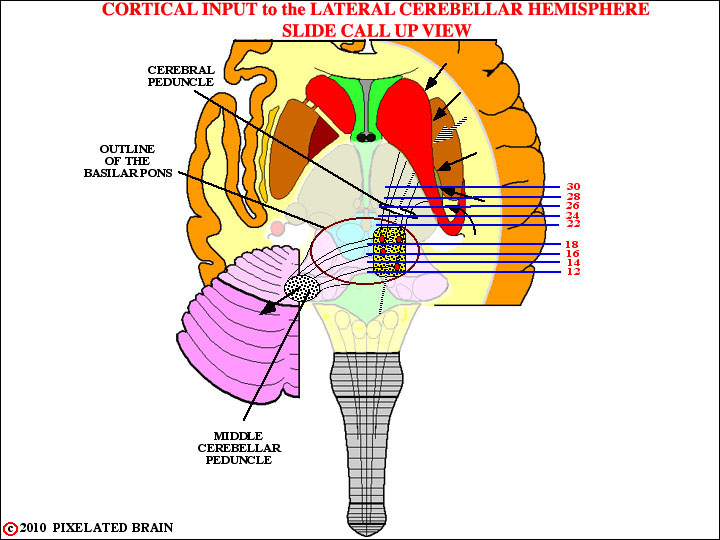
Now we will trace these descending fibers downward, toward the basilar pons. Refer back to this view for orientation, as you go through the slides that follow.
 Descending fibers of the corticopontine pathways, separated by the corticospinal tract, are now passing around the thalamus in the internal capsule to reach the ventral surface of the midbrain.
Descending fibers of the corticopontine pathways, separated by the corticospinal tract, are now passing around the thalamus in the internal capsule to reach the ventral surface of the midbrain.
Frontopontine fibers and the corticospinal tract have now entered the cerebral peduncle, which lies on the ventral surface of the midbrain. The remaining fibers of the descending cerebellar pathways are still in the internal capsule, but will reach the peduncle shortly.
 Frontopontine fibers and the corticospinal tract have now entered the cerebral peduncle, which lies on the ventral surface of the midbrain. The remaining fibers of the descending cerebellar pathways are still in the internal capsule, but will reach the peduncle shortly.
Frontopontine fibers and the corticospinal tract have now entered the cerebral peduncle, which lies on the ventral surface of the midbrain. The remaining fibers of the descending cerebellar pathways are still in the internal capsule, but will reach the peduncle shortly.
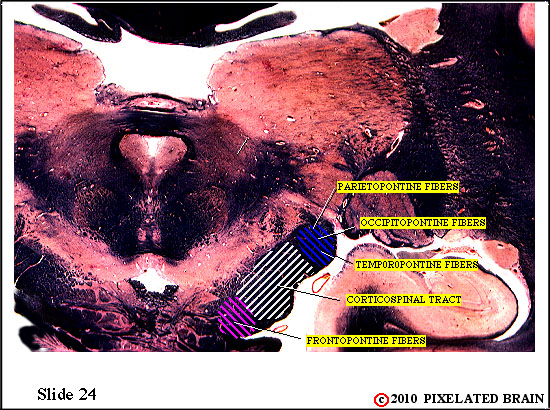
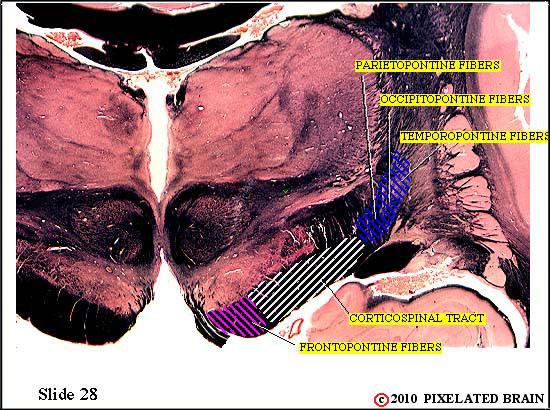
 This is the best view we will get of the cerebral peduncle, because at more caudal levels the fibers in the medial edge of the peduncle will pass into the basilar pons. In fact, as the sagittal view shows, the bottom of the slide passes through the rostral tip of the basilar pons.
This is the best view we will get of the cerebral peduncle, because at more caudal levels the fibers in the medial edge of the peduncle will pass into the basilar pons. In fact, as the sagittal view shows, the bottom of the slide passes through the rostral tip of the basilar pons.
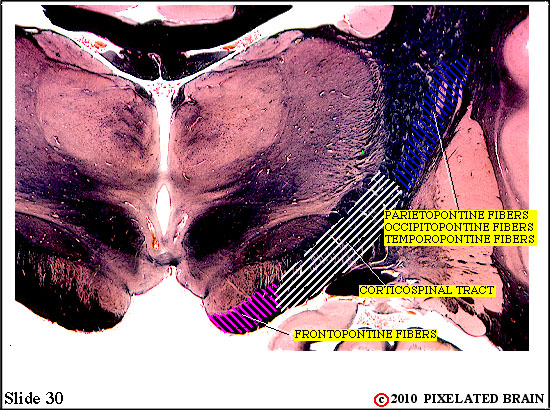
Frontopontine fibers are said to form the medial fifth of the peduncle. Parieto-, temporo- and occipito-pontine fibers are said to occupy the lateral fifth and the middle three fifths of the peduncle is where the corticospinal tract runs.
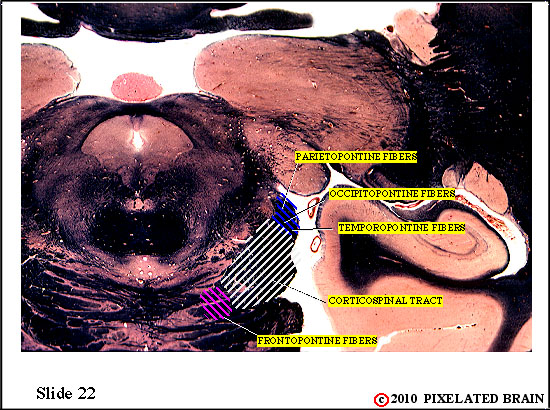
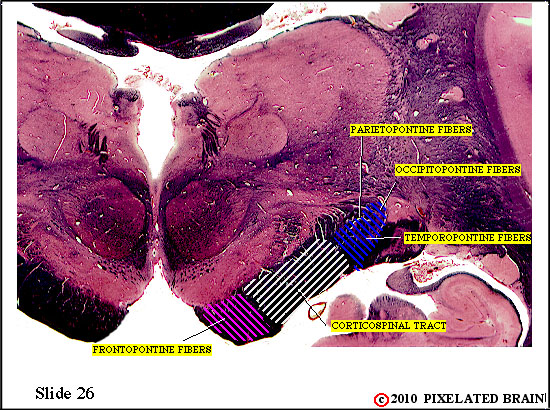
 The pathways that have descended through the cerebral peduncle are now entering the basal pons.
The pathways that have descended through the cerebral peduncle are now entering the basal pons.
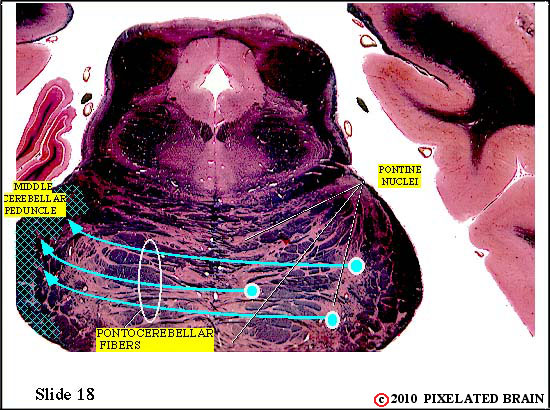
 Within the basilar pons corticopontine fibers terminate on neurons in the pontine nuclei. These neurons , in turn, give rise to axons which cross the midline and enter the middle cerebellar peduncle. These pontocerebellar axons will terminate as mossy fibers within the lateral part of the cerebellum (the cerebrocerebellum).
Within the basilar pons corticopontine fibers terminate on neurons in the pontine nuclei. These neurons , in turn, give rise to axons which cross the midline and enter the middle cerebellar peduncle. These pontocerebellar axons will terminate as mossy fibers within the lateral part of the cerebellum (the cerebrocerebellum).
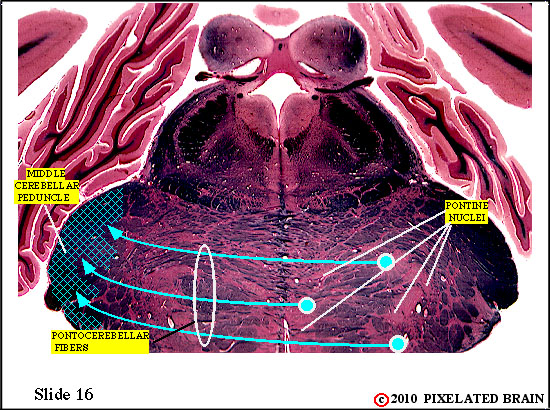
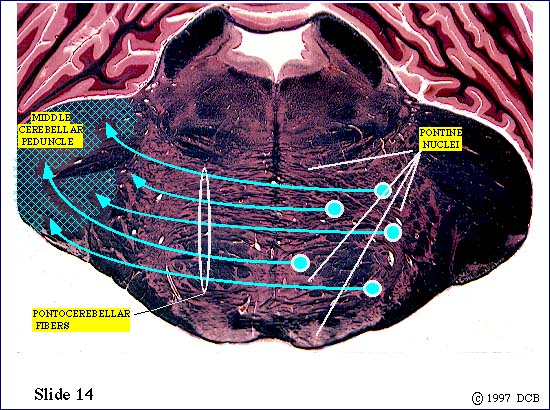
 Within the basilar pons corticopontine fibers terminate on neurons in the pontine nuclei. These neurons , in turn, give rise to axons which cross the midline and enter the middle cerebellar peduncle. These pontocerebellar axons will terminate as mossy fibers within the lateral part of the cerebellum (the cerebrocerebellum).
Within the basilar pons corticopontine fibers terminate on neurons in the pontine nuclei. These neurons , in turn, give rise to axons which cross the midline and enter the middle cerebellar peduncle. These pontocerebellar axons will terminate as mossy fibers within the lateral part of the cerebellum (the cerebrocerebellum).
Unfortunately, our slides cut through the peduncle in an oblique manner, and we never see all of it in a single slide.
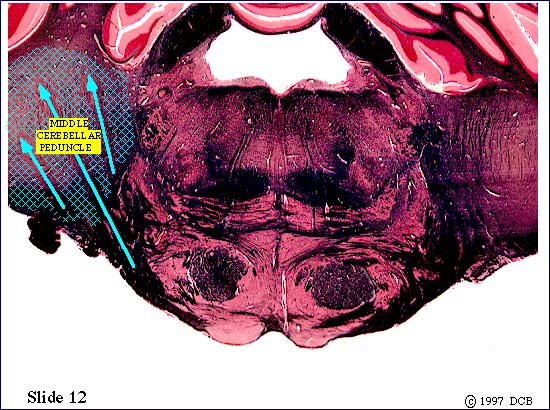
Within the basilar pons corticopontine fibers terminate on neurons in the pontine nuclei. These neurons , in turn, give rise to axons which cross the midline and enter the middle cerebellar peduncle. These pontocerebellar axons will terminate as mossy fibers within the lateral part of the cerebellum (the cerebrocerebellum).
Unfortunately, our slides cut through the peduncle in an oblique manner, and we never see all of it in a single slide.
Formation of the middle cerebellar peduncle is now almost complete, and this is the last slide of this series.