MODULE 7 - SECTION 2 - WHAT ARE THR BASAL GANGLIA?
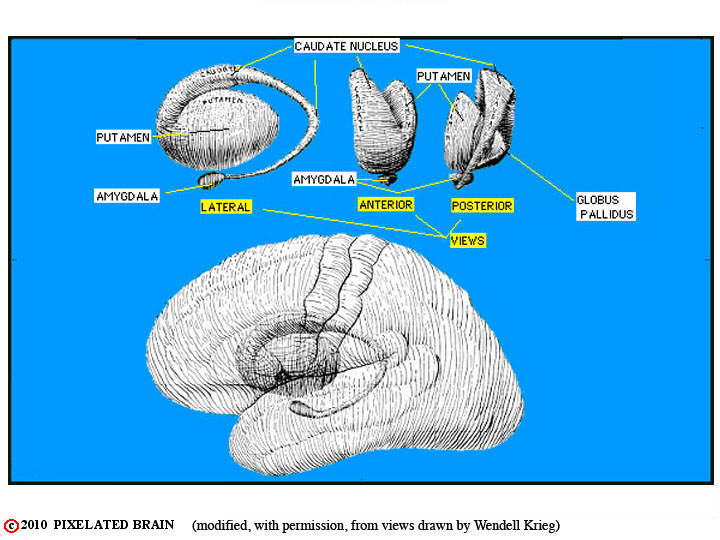
The name Basal Ganglia was originally given, more than a century ago, to a group of cellular structures buried deep within the cerebral hemisphere. It was an anatomical designation, not a functional one, and the figure below shows this group of structures - the caudate nucleus, the putamen, the globus pallidus and the amygdala. Interest in the basal ganglia has increased enormously over the past 50 years as we have come understand more about their role in controlling motor function. Parkinson's disease and Huntington's disease are but two of the many motor disorders associated with disease of the basal ganglia. As researchers have focused on these disorders, they have come to define the basal ganglia in functional terms rather than anatomical ones. Thus the modern definition of the basal ganglia includes three nuclei within the hemisphere - the caudate nucleus, the putamen and the globus pallidus - and two closely related structures - the subthalamic nucleus and the substantia nigra. Blumenfeld shows this in his Table 16.1. As he points out, the caudate nucleus and the putamen, together are called the striatum; the putamen and globus pallidus, together, are sometimes called the lentiform nucleus.