TRIGEM



29
|
TRIGEM
|
||
 |
 |
|
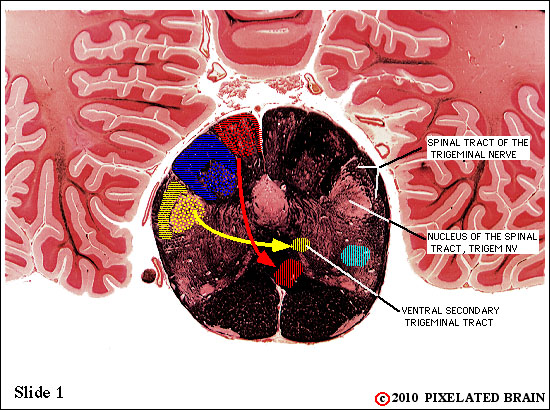
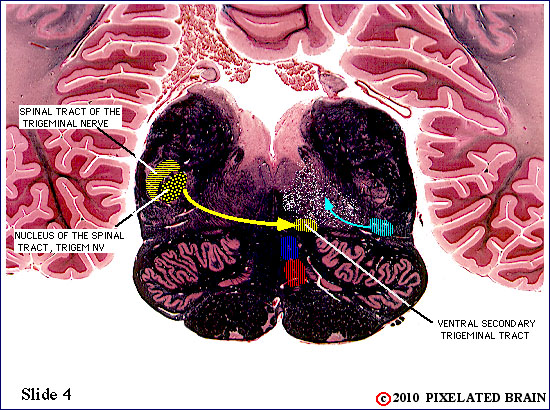
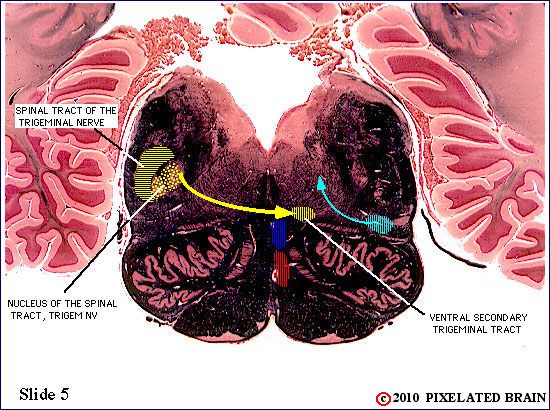
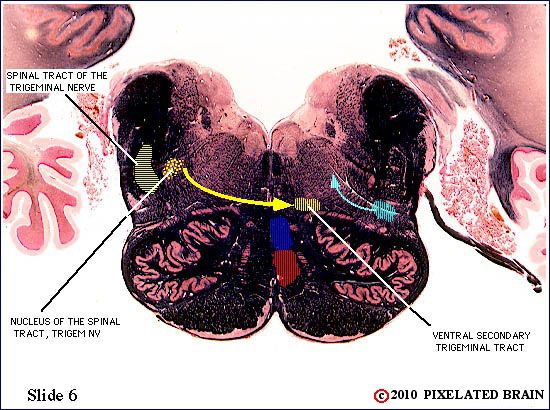
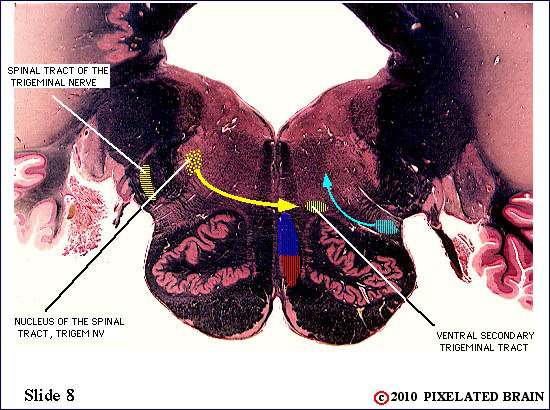
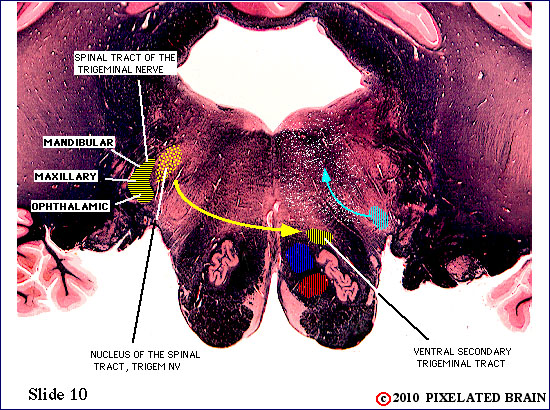
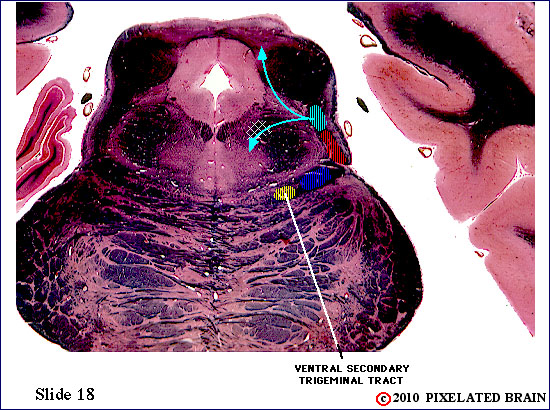
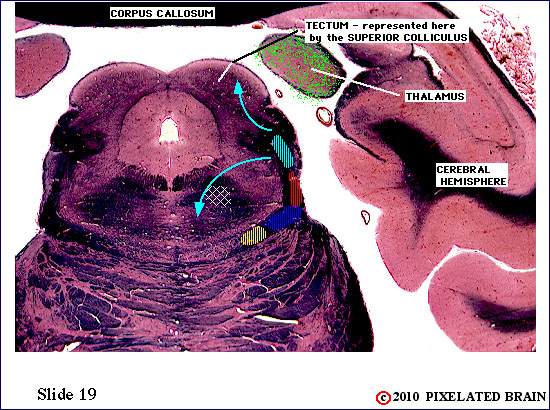
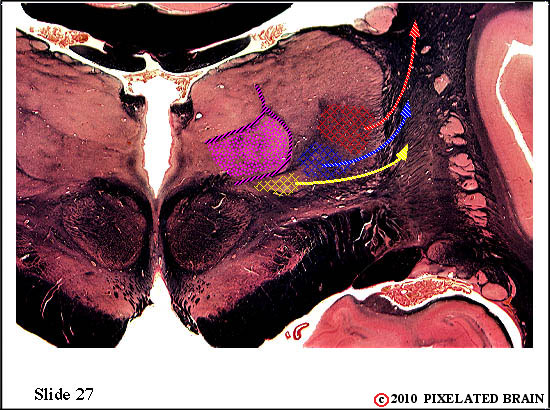
| The spinal tract of the trigeminal nerve (horizontal yellow shading) is composed of axons that have their cell bodies in the trigeminal (semilunar) ganglion. This pathway conveys sensations of pain and temperature from the face. The axons will terminate on second order neurons of the pathway that lie within the nucleus of the spinal tract of the trigeminal nerve - represented here by yellow stippling. Neurons in the nucleus give rise to the ventral secondary trigeminal tract, which is shown here crossing the midline to ascend to the nucleus ventralis posteromedialis (VPM) of the thalamus. | ||
 |
 |
|
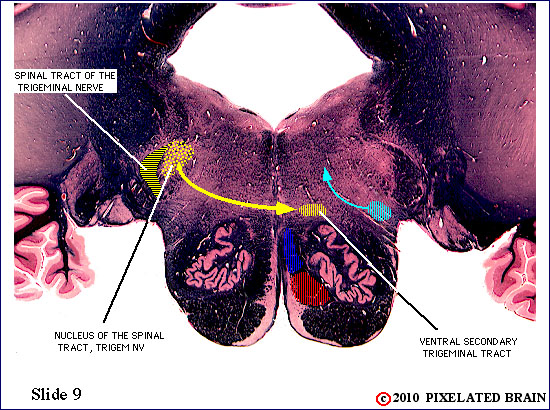
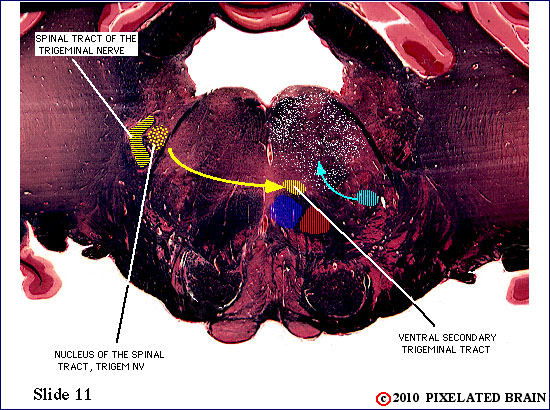
| The spinal tract of the trigeminal nerve (horizontal yellow shading) is composed of axons that have their cell bodies in the trigeminal (semilunar) ganglion. This pathway conveys sensations of pain and temperature from the face. The axons will terminate on second order neurons of the pathway that lie within the nucleus of the spinal tract of the trigeminal nerve - represented here by yellow stippling. Neurons in the nucleus give rise to the ventral secondary trigeminal tract, which is shown here crossing the midline to ascend to the nucleus ventralis posteromedialis (VPM) of the thalamus. | ||
 |
 |
|
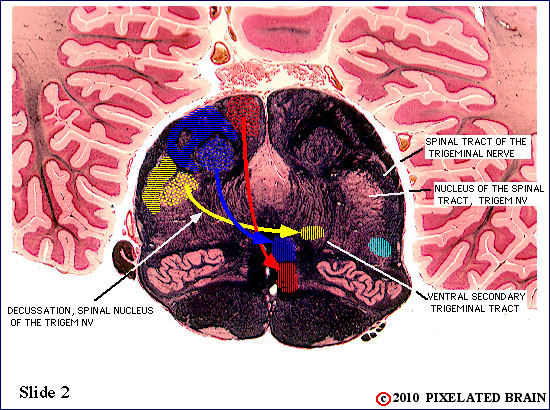
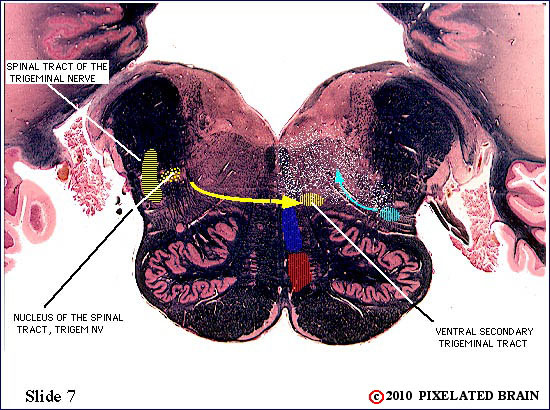
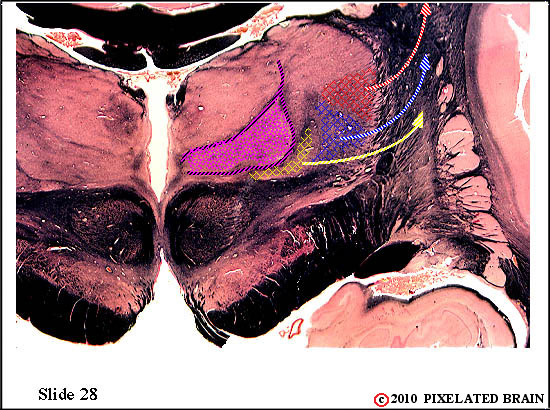
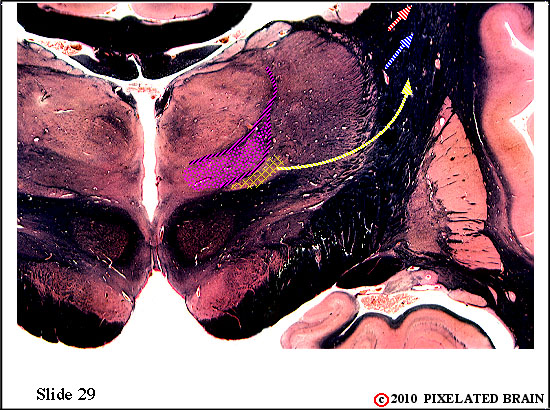
| The spinal tract of the trigeminal nerve (horizontal yellow shading) is composed of axons that have their cell bodies in the trigeminal (semilunar) ganglion. This pathway conveys sensations of pain and temperature from the face. The axons will terminate on second order neurons of the pathway that lie within the nucleus of the spinal tract of the trigeminal nerve - represented here by yellow stippling. Neurons in the nucleus give rise to the ventral secondary trigeminal tract, which is shown here crossing the midline to ascend to the nucleus ventralis posteromedialis (VPM) of the thalamus. The somatotopec organization of the spinal tract is shown in this view. | ||
 |
 |
|
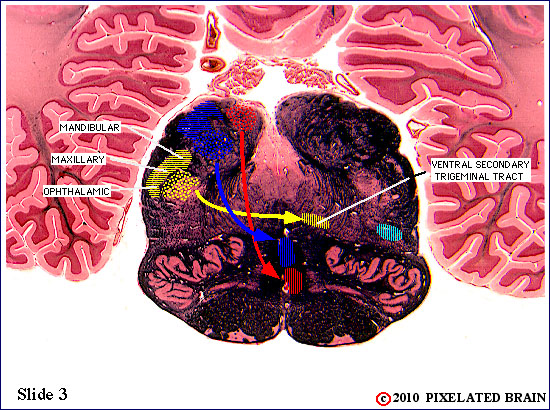
| The spinal tract of the trigeminal nerve (horizontal yellow shading) is composed of axons that have their cell bodies in the trigeminal (semilunar) ganglion. This pathway conveys sensations of pain and temperature from the face. The axons will terminate on second order neurons of the pathway that lie within the nucleus of the spinal tract of the trigeminal nerve - represented here by yellow stippling. Neurons in the nucleus give rise to the ventral secondary trigeminal tract, which is shown here crossing the midline to ascend to the nucleus ventralis posteromedialis (VPM) of the thalamus. | ||
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
|
| The spinal tract of the trigeminal nerve (horizontal yellow shading) is composed of axons that have their cell bodies in the trigeminal (semilunar) ganglion. This pathway conveys sensations of pain and temperature from the face. The axons will terminate on second order neurons of the pathway that lie within the nucleus of the spinal tract of the trigeminal nerve - represented here by yellow stippling. Neurons in the nucleus give rise to the ventral secondary trigeminal tract, which is shown here crossing the midline to ascend to the nucleus ventralis posteromedialis (VPM) of the thalamus. | ||
 |
 |
|
| The spinal tract of the trigeminal nerve (horizontal yellow shading) is composed of axons that have their cell bodies in the trigeminal (semilunar) ganglion. This pathway conveys sensations of pain and temperature from the face. The axons will terminate on second order neurons of the pathway that lie within the nucleus of the spinal tract of the trigeminal nerve - represented here by yellow stippling. Neurons in the nucleus give rise to the ventral secondary trigeminal tract, which is shown here crossing the midline to ascend to the nucleus ventralis posteromedialis (VPM) of the thalamus. | ||
 |
 |
|
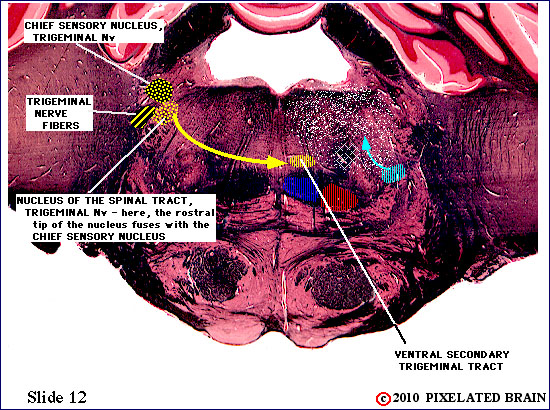
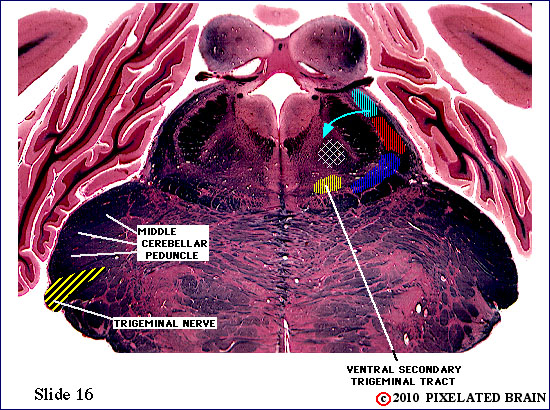
| Trigeminal nerve fibers have passed medially through the middle cerebellar peduncle to reach the region of the sensory (and motor) nuclei associated with this nerve. Some of the sensory fibers will turn caudally and descend in the spinal tract of the trigeminal nerve. Others will terminate at this level, in the chief sensory nucleus, or the rostral tip of the nucleus of the spinal tract. Both nuclei contribute fibers to the pathway that crosses the midline and ascends as the ventral secondary trigeminal tract. | ||
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
|
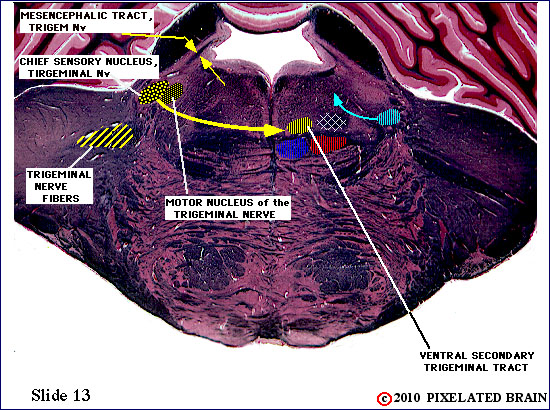
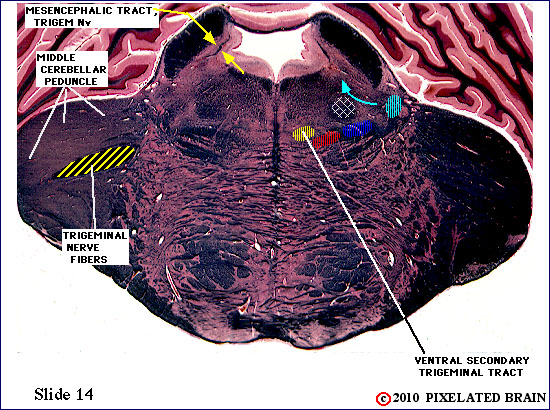
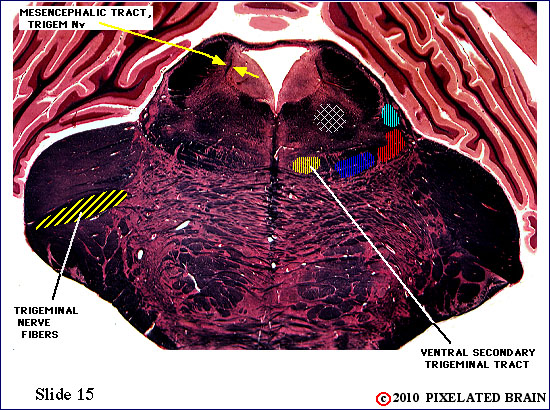
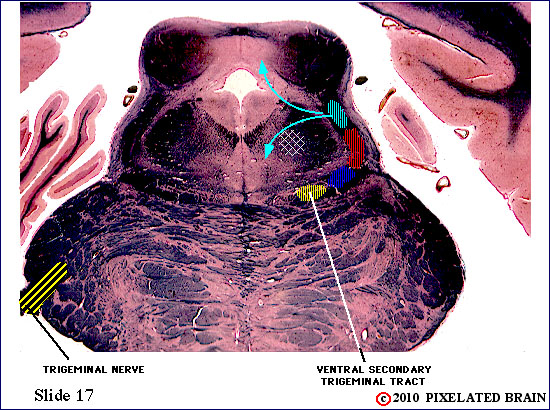
| The fibers of the trigeminal nerve can be seen passing medially, through the middle cerebellar peduncle, but this slide lies just rostral to the chief sensory nucleus of the nerve. The ventral secondary trigeminal tract is now completely formed, and ascends to the thalamus on the contralateral side of the brainstem. Fibers can be seen passing to and from the mesencephalic nucleus in the mesencephalic tract. The nucleus, itself, consists of a small scattering of cells surrounding the tract. | ||
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
|
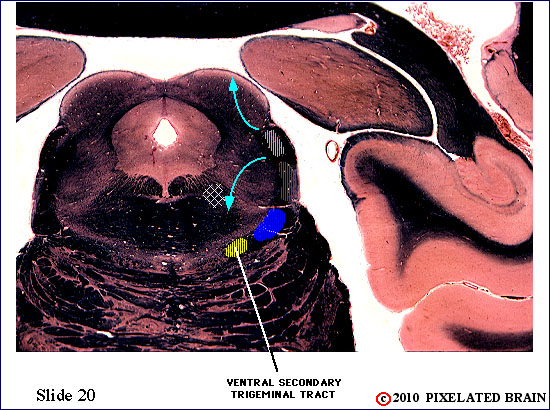
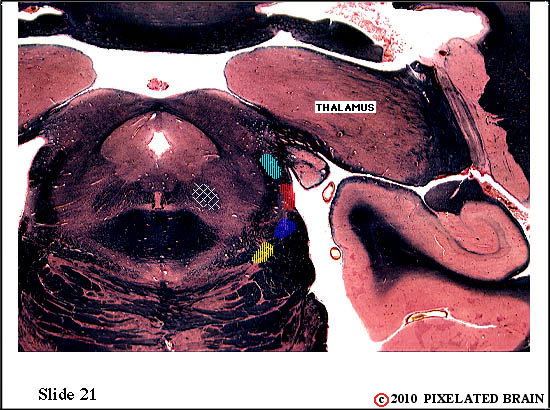
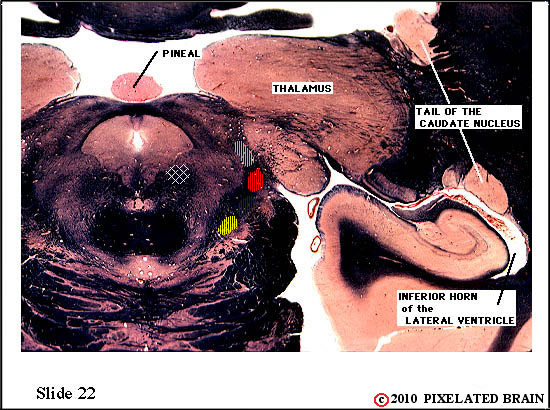
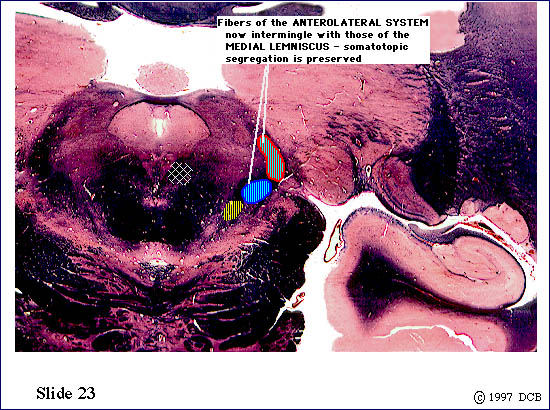
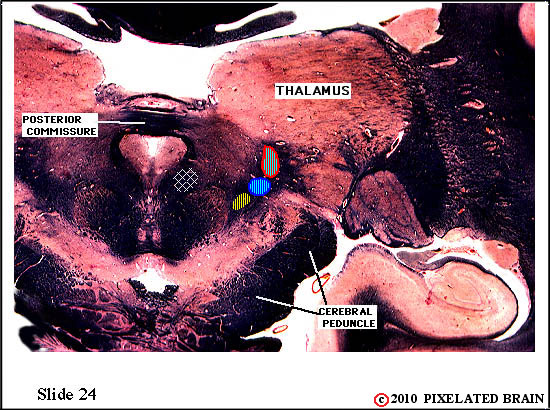
| The ventral secondary tract lies near the medial edge of the medial lemniscus It contains the axons of second order neurons. The tract ascends to the thalamus, where axons will terminate on third order neurons within the nucleus ventralis posteromedialis (VPM). | ||
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
|
| The ventral secondary trigeminal tract lies near the medial edge of the medial lemniscus. It contains the axons of second order neurons. The tract ascends to the thalamus, where the axons will terminate on third order neurons within the nucleus ventralis posteromedialis (VPM). | ||
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
|
29 |
||