CORTICOSPINAL TRACT in the BASILAR PONS
x- PIXBRAIN HOME _ _ MOD 5 HOME _ _ I WANT TO -x
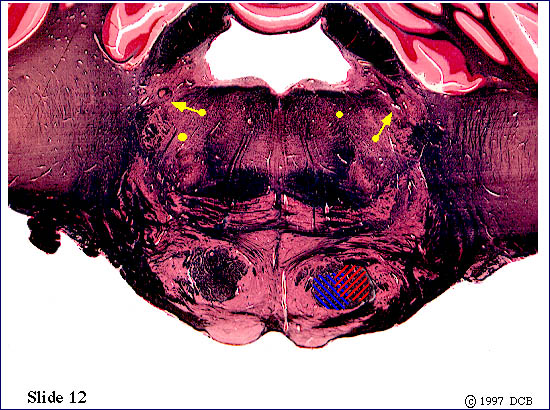
The corticospinal fibers are still in the basilar pons, and the corticbulbar ones in the tegmentum (of the pons). A look at the view of slide 12 of the Brainstem Atlas tells you that this slide passes through the motor nucleus of the trigeminal nerve. Within this nucleus are the "lower motor neurons" that innervate the muscles of mastication - the ones you use to chew and bite. The neurons of this nucleus must receive an input from "upper motor neurons" within the "head" area of the motor cortex. We have been representing the descending axons of these neurons by the
yellow dots, and now some of them will terminate within the motor nucleus of the trigeminal nerve. Unlike the corticospinal pathway, which is almost entirely crossed, the corticobulbar one has both crossed and uncrossed components. Think, a bit, about just what this means, in terms of brain function and the effect of lesions of the corticbulbar pathway. Click on "key" to look at the next (rostral or caudal) slide. Click on the red ball to return to the text, by way of the call-up view)