PIXBRAIN HOME _ _ MOD 1 HOME _ _ previous _ _ FIGDEV-1-2 _ _ next _ _ I WANT TO
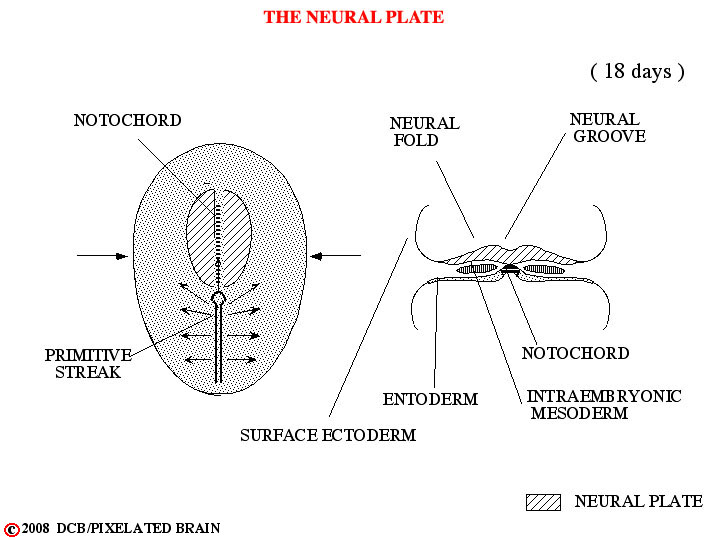
- - In the first few days following fertilization of the ovum, the single celled zygote divides repeatedly to form a solid cell mass of 12 - 16 cells called a morula. During the second week of development this structure implants in the wall of the uterus. Two cavities now develop within the mass - the amnionic cavity above and the yolk sac below. Between these two lies the embryonic bilaminar disc, consisting of a layer of ectoderm lying above a layer of entoderm. During the third week of development a region termed the primitive streak forms on the dorsal surface of the disc, giving a longitudinal axis to the developing embryo. Cells from the surface of the disc migrate through this region and then spread out between the ectoderm and the entoderm to create a new cell layer. The cells that migrate laterally form mesoderm, thus transforming the bilaminar disc into a trilaminar one. Other cells migrate anteriorly in the midline to form the notocord. By a process of neural transduction, the notocord induces the overlying ectoderm to become neural tissue - the neural plate. In the midline, just above the notocord, a neural groove forms. Lateral to this on either there is a proliferation of neural ectoderm to form neural folds.