MODULE 2 - SECTION 5 - DIVISIONS of the BRAINSTEM
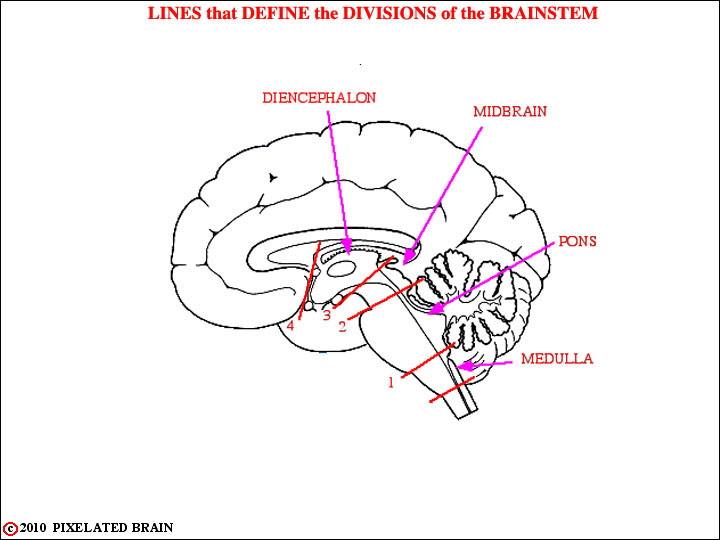
You are now ready to put your knowledge of surface anatomy to use in identifying the level of cross sections through the brainstem. The lines in this figure serve to define the borders between divisions of the brainstem.
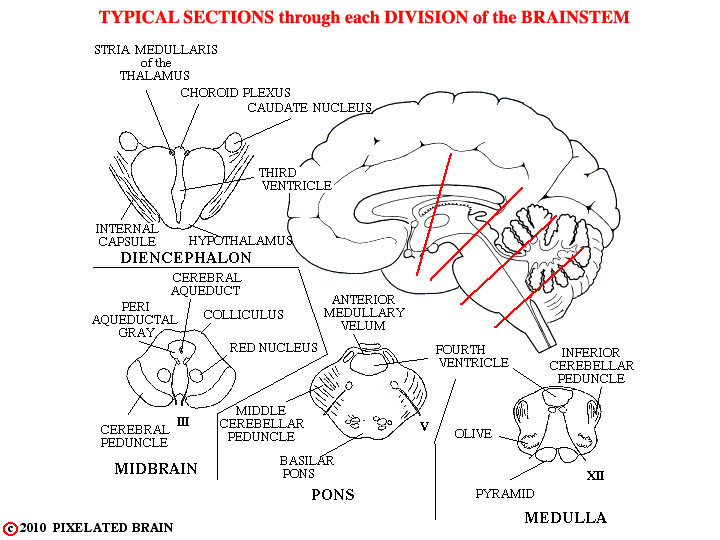
The 4 lines drawn on the mid-sagittal view here show the plane of cut for the sections in the figure. In each section, a few of the landmarks that help to identify the level of the section are given.
For example, the presence of the colliculi, the cerebral aqueduct and the cerebral peduncle in the section shown in the lower left part of the figure tell you that this section HAS TO BE through the midbrain. However, because the slides in our slide series cut through most of the brainstem at an oblique angle, we will rarely sections that look exactly like these "typical" ones.
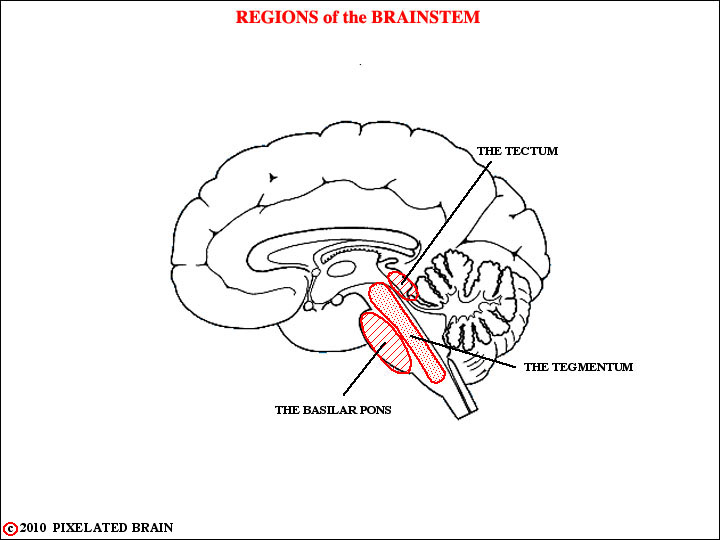
Before you look at the slides we also want to introduce you to three terms that we will use starting with Module 3. They are shown here in our mid-sagittal view of the brainstem
The TEGMENTUM refers to the central core of the brainstem that extends from the medulla through the midbrain. Most (but not all) of the ascending sensory and descending motor pathways of the brain pass through this region. Cranial nerve nuclei are found here and a diffuse collection of neurons, called the reticular formation, occupies much of this region.
At the pontine level, a large mass of neural tissue, called the BASILAR PONS, lies ventral to the tegmentum. We will discuss it when we do the cerebellum.
At the midbrain level, the TECTUM lies dorsal to the tegmentum. It consists of the superior and inferior colliculi.
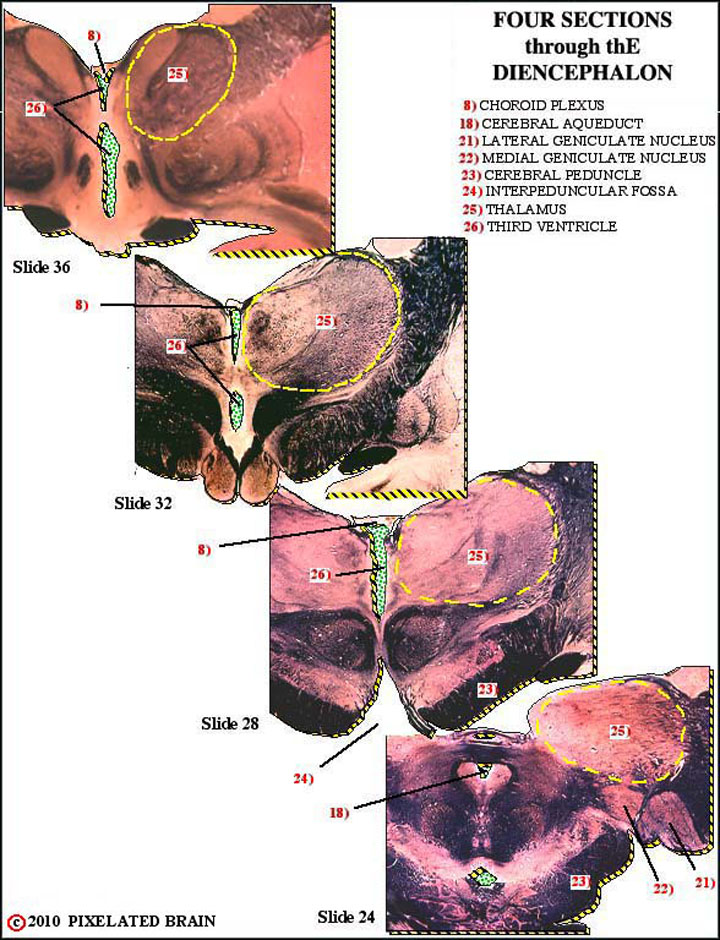
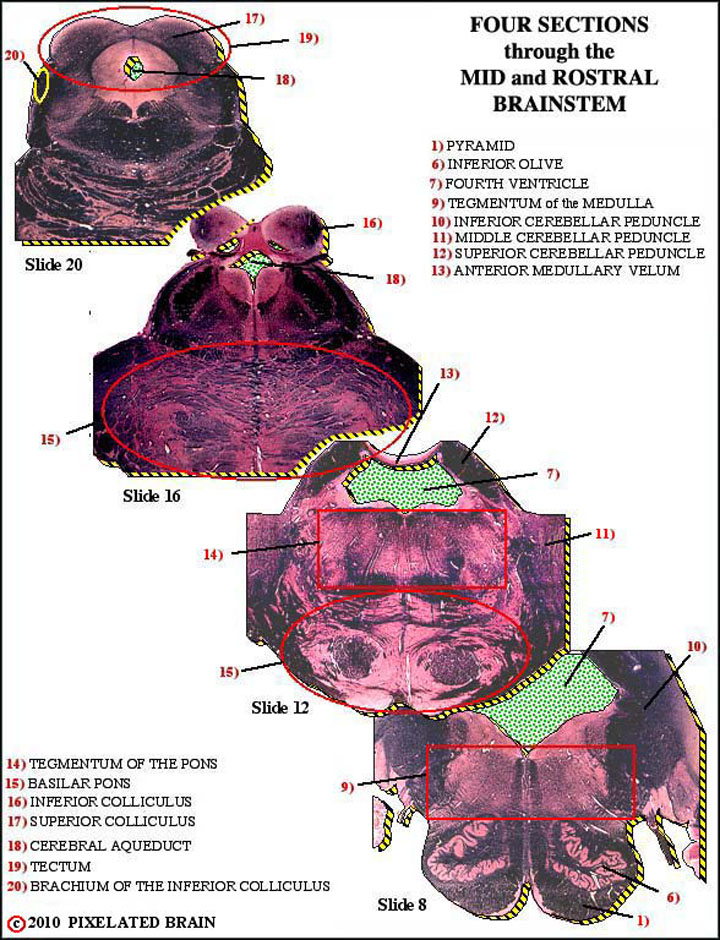
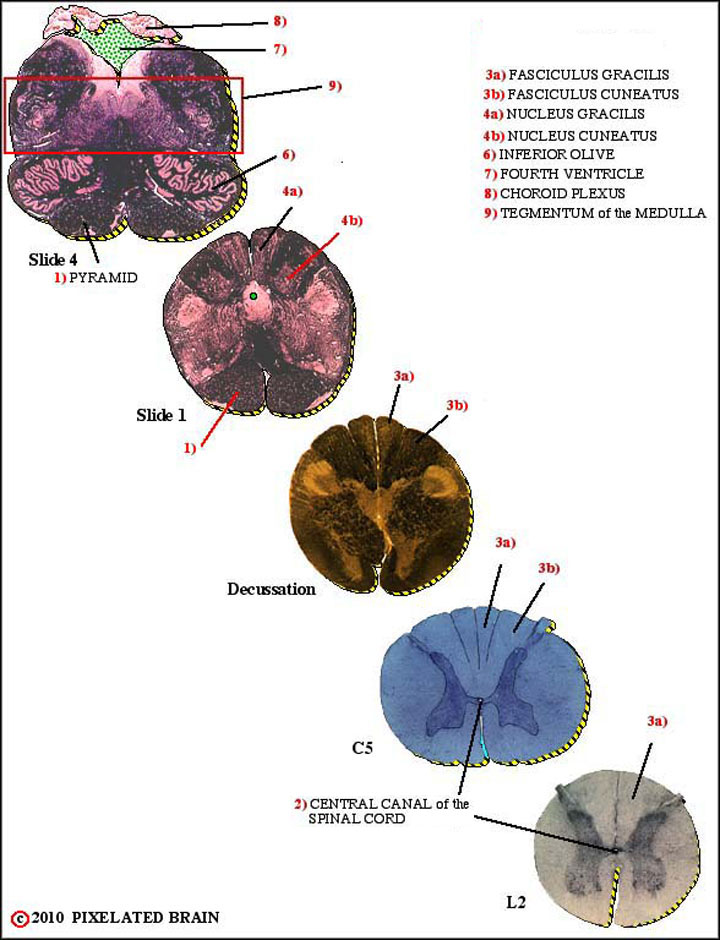
Below are 25 structures or spaces, which are labelled in the composite images to the left. Click on the structure names for more details.
8) CHOROID PLEXUS - forms a roof for the third and fourth ventricles; secretes some CSF
18) CEREBRAL AQUEDUCT - connects the third and fourth ventricles
21) LATERAL GENICULATE NUCLEUS - part of the visual pathway - most optic tract fibers terminate here
22) MEDIAL GENICULATE NUCLEUS - part of the auditory pathway
23) CEREBRAL PEDUNCLE - contains descending motor fibers, and a pathway from the cerebral cortex to the cerebellum
24) INTERPEDUNCULAR FOSSA - a space
25) THALAMUS - part of the diencephalon
26) THIRD VENTRICLE - CSF enters from the lateral ventricles and exits by way of the cerebral aqueduct
1) PYRAMID - part of the major descending motor pathway
6) INFERIOR OLIVE - neurons here send axons to the cerebellum through the inferior cerebellar peduncle
7) FOURTH VENTRICLE - the most caudal of the ventricles; CSF enters it by descending through the cerebral aqueduc
9) TEGMENTUM OF THE MEDULLA - ascending pathways, descending pathways, the reticular formation and cranial nerve structures are found here
10) INFERIOR CEREBELLAR PEDUNCLE - carries input to the cerebellum from the spinal cord and inferior olve
11) MIDDLE CEREBELLAR PEDUNCLE - carries input to the cerebellum from the cerebral cortex
12) SUPERIOR CEREBELLAR PEDUNCLE - the output pathway for the cerebellum
13) ANTERIOR MEDULLARY VELUM - passes between the two superior cerebellar peduncles and forms a roof over the anterior part of the fourth ventricle
14) TEGMENTUM OF THE PONS - see 9)
15) BASILAR PONS - lies "underneath" the tegmentum of the pons - contains descending motor fibers and nuclei that send axons to the cerebellum by way of the middle cerebellar peduncle
16) INFERIOR COLLICULUS - part of the ascending auditory pathway
17) SUPERIOR COLLICULUS - part of the visual system
18) CEREBRAL AQUEDUCT - connects the third and fourth ventricles
19) TECTUM - name for the region containing the superior and inferior colliculi
20) BRACHIUM OF THE INFERIOR COLLICULUS - part of the auditory pathway
2) CENTRAL CANAL of SPINAL CORD - will open into the fourth ventricle shortly
3a) FASCICULUS GRACILIS
3b) FASCICULUS CUNEATUS - part of a major ascending sensory pathway from the upper body
4a) NUCLEUS GRACILIS - part of a major ascending sensory pathway from the lower body
4b) NUCLEUS CUNEATUS
6) INFERIOR OLIVE - neurons here send axons to the cerebellum through the inferior cerebellar peduncle
7) FOURTH VENTRICLE - the most caudal of the ventricles; CSF enters it by descending through the cerebral aqueduct
8) CHOROID PLEXUS - forms a roof for the third and fourth ventricles; secretes some CSF
9) TEGMENTUM OF THE MEDULLA - ascending pathways, descending pathways, the reticular formation and cranial nerve structures are found here